Appearance
Table of Contents generated with DocToc
This is not for rookie, we'll introduce something about more advanced.
Merge with Rebase
This command shows no difference with the command merge.
We usually use merge to merge the code from one branch to master , like this:
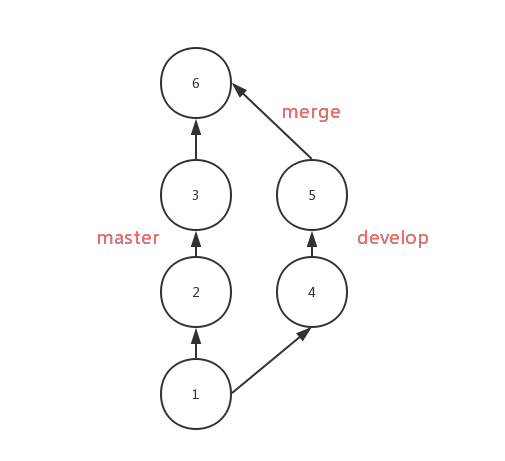
After using rebase , the commits from develop will be moved to the third commit of the master in order, as follows:
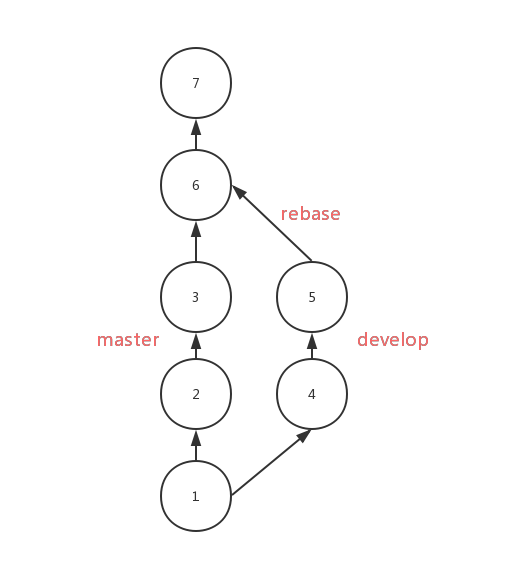
Compare with merge, the result of rebase is very clear with a single flow. But if there is any conflict, you'll be in trouble to solving them. You have to solve them one by one , while you only need to solve them one-time if using merge.
You should use rebase on the local branchs which need be rebased. If you need to rebase the develop to the master, you should do as follows:
shell
## branch develop
git rebase master
git checkout master
## move HEAD on `master` to the latest commit
git merge developstash
Use git stash to save the current state of the working directory while you want to check out branch, if you don't want to use commit.
shell
git stashThis command can record the current state of the working directory, if you want to recover it, you can do like this:
shell
git stash popthen you'll back to the exactly state before.
reflog
This command will show you the records of HEAD's trace. If you delete a branch by mistake, you can examine the hashs of HEAD by using reflog.
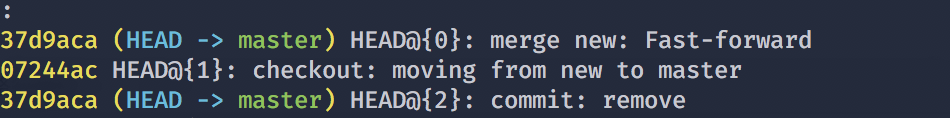
According to the picture, the last movement of HEAD is just after merge, and then the new branch was deleted, so we can get the branch back by the following command:
shell
git checkout 37d9aca
git checkout -b newPS:reflog is time-bound, it can only record the state over a period of time.
Reset
If you want to delete the last commit, you can do like this:
shell
git reset --hard HEAD^But this command doesn't delete the commit, it just reset the HEAD and branch.
